Rare earth elements are known as the "vitamins of industry" and have irreplaceable excellent magnetic, optical, and electrical properties. They play a huge role in improving product performance, increasing product variety, and improving production efficiency. Due to its high activity and low usage, rare earths have become an important element for improving product structure, increasing technological content, and promoting industry technological progress. They are widely used in metallurgy, military, petrochemicals, glass ceramics, agriculture, and new materials.

Rare earth elements are known as the "vitamins of industry" and have irreplaceable excellent magnetic, optical, and electrical properties. They play a huge role in improving product performance, increasing product variety, and improving production efficiency. Due to its high activity and low usage, rare earths have become an important element for improving product structure, increasing technological content, and promoting industry technological progress. They are widely used in metallurgy, military, petrochemicals, glass ceramics, agriculture, and new materials.
Metallurgical industry

Rare earth has been applied in the field of metallurgy for more than 30 years, and has formed relatively mature technologies and processes. The application of rare earth in steel and non-ferrous metals is a large-scale and wide-ranging field with broad prospects. Adding rare earth metals, fluorides, and silicides to steel can refine, desulfurize, neutralize low melting point harmful impurities, and improve the processing performance of steel; Rare earth ferrosilicon alloy and rare earth silicon magnesium alloy are used as spheroidizing agents to produce rare earth nodular cast iron. Due to their special suitability for producing complex nodular iron parts with special requirements, these nodular cast irons are widely used in mechanical manufacturing industries such as automobiles, tractors, and diesel engines; Adding rare earth metals to non-ferrous alloys such as magnesium, aluminum, copper, zinc, and nickel can improve the physical and chemical properties of the alloys, as well as enhance their mechanical properties at room temperature and high temperature.
Military field

Due to its excellent physical properties such as optoelectronics and magnetism, rare earths can be combined with other materials to form a variety of new materials with different properties, greatly improving the quality and performance of other products. Therefore, it is known as "industrial gold". Firstly, the addition of rare earths can significantly improve the tactical performance of steel, aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, and titanium alloys used for manufacturing tanks, aircraft, and missiles. In addition, rare earths can also be used as lubricants for many high-tech industries such as electronics, lasers, nuclear industry, superconductivity, etc. Once rare earth technology is used for military purposes, it will inevitably bring about a leap in military technology. In a certain sense, the US military's overwhelming control in several local wars after the Cold War, as well as its ability to openly kill enemies without restraint, are due to its rare earth technology superhuman.
Petrochemical industry

Rare earth elements can be used to make molecular sieve catalysts in the petrochemical industry, which have the advantages of high activity, good selectivity, and strong resistance to heavy metal poisoning. Therefore, they have replaced aluminum silicate catalysts for petroleum catalytic cracking processes; In the production process of synthetic ammonia, a small amount of rare earth nitrate is used as a co catalyst, and its gas processing capacity is 1.5 times larger than that of nickel aluminum catalyst; In the process of synthesizing butadiene rubber and isoprene rubber, the use of rare earth cycloalkanoate triisobutylaluminum catalyst results in excellent product performance, with advantages such as less equipment adhesion, stable operation, and short post-processing steps; Composite rare earth oxides can also be used as catalysts for exhaust gas purification in internal combustion engines, and cerium cycloalkanoate can also be used as paint drying agents.
Glass ceramics

The application of rare earth elements in China's glass and ceramic industry has been increasing at an average rate of 25% since 1988, reaching about 1600 tons in 1998. Rare earth glass and ceramics are not only traditional basic materials for industry and life, but also major members of the high-tech field. Rare earth oxides or processed rare earth concentrates can be widely used as polishing powders for polishing optical glass, eyeglass lenses, picture tubes, oscilloscopes, flat glass, plastics, and metal tableware; During the process of melting glass, cerium dioxide can be utilized to have a strong oxidizing effect on iron, reducing the iron content in the glass and achieving the goal of removing green from the glass; Adding rare earth oxides can produce optical glass and special glass for different purposes, including glass that can pass infrared and absorb ultraviolet radiation, acid and heat resistant glass, X-ray resistant glass, etc; Adding rare earth elements to ceramic and porcelain glazes can reduce the fragmentation of glazes and give products different colors and luster, which is widely used in the ceramic industry.
In terms of agriculture

The research results indicate that rare earth elements can increase the chlorophyll content of plants, enhance photosynthesis, promote root development, and increase nutrient absorption by roots. Rare earth elements can also promote seed germination, increase seed germination rate, and promote seedling growth. In addition to the main functions mentioned above, it also has the ability to enhance the disease resistance, cold resistance, and drought resistance of certain crops. Numerous studies have also shown that the use of appropriate concentrations of rare earth elements can promote the absorption, transformation, and utilization of nutrients by plants. Spraying rare earth elements can increase the Vc content, total sugar content, and sugar acid ratio of apple and citrus fruits, promoting fruit coloring and early ripening. And it can suppress the respiratory intensity during storage and reduce the decay rate.
New materials field
Rare earth neodymium iron boron permanent magnet materials have characteristics such as high remanence, high coercivity, and high magnetic energy product, and are widely used in the electronics and aerospace industries and to drive wind turbines (especially suitable for offshore power plants); Garnet type ferrite single crystals and polycrystals composed of pure rare earth oxides and ferric oxide can be used in the microwave and electronics industries; Yttrium aluminum garnet and neodymium glass made of high-purity neodymium oxide can be used as solid laser materials; Rare earth hexaborides can be used to make cathode materials for electron emission; Lanthanum nickel metal is a newly developed hydrogen storage material in the 1970s; Lanthanum chromate is a high-temperature thermoelectric material; Currently, countries around the world have made breakthroughs in the development of superconducting materials by using barium based oxides improved with barium yttrium copper oxygen elements, which can obtain superconductors in the liquid nitrogen temperature range. In addition, rare earths are widely used in lighting sources such as fluorescent powders, intensifying screen fluorescent powders, tricolor fluorescent powders, and photocopy lamp powders (but their application in lighting is gradually decreasing due to the high cost caused by the rise in rare earth prices), projection televisions, tablets, and other electronic products; In agriculture, applying trace amounts of rare earth nitrate to crops in the field can increase their yield by 5-10%; In the textile industry, rare earth chlorides are also widely used in tanning fur, fur dyeing, yarn dyeing, and carpet dyeing; Rare earth elements used in automotive catalytic converters can convert major pollutants into non-toxic compounds during engine exhaust.
Other applications
Rare earth elements are also applied in various digital products, including audiovisual, photography, and communication devices, meeting multiple requirements such as smaller, faster, lighter, longer lasting, and energy-efficient products. At the same time, it has also been applied to multiple fields such as green energy, healthcare, water purification, and transportation.
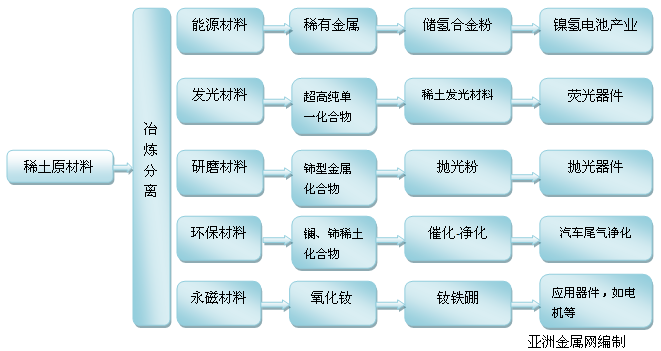
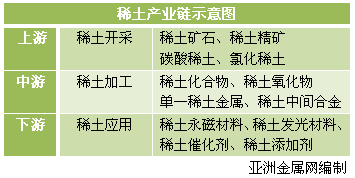
Rare earth industry chain
Schematic diagram of rare earth industry chain
The application fields of 17 rare earth elements are shown in the following figure:

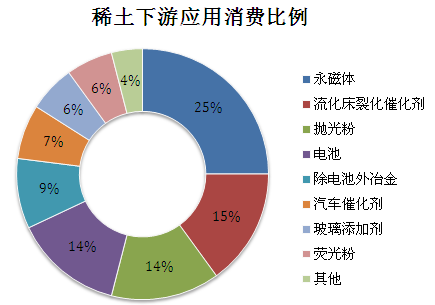
Divided by downstream applications, the consumption ratio is as follows: