
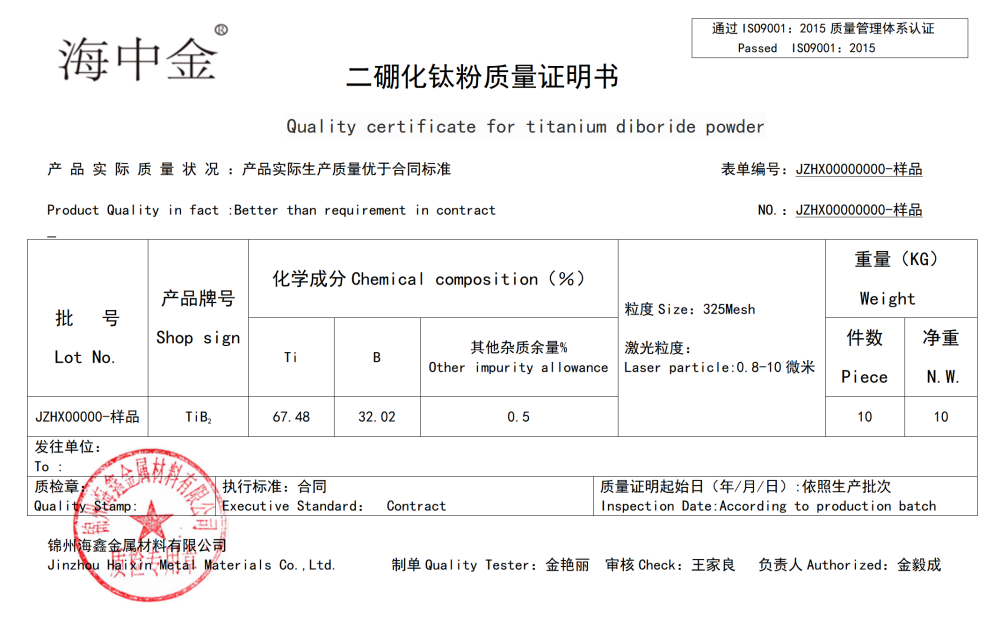
Product Name: Titanium Diboride (TiB2)
Specification: 0.8-10um (D50)
Appearance: Irregular
Color: Black Grey
Features: high melting point, high hardness, wear resistance, low friction coefficient, excellent mechanical properties, thermal conductivity
Usage: Aerospace, automotive manufacturing, high-temperature ceramic cutting tools and cutting tools, thermal management, electronic devices, ceramic bulletproof plates and other fields


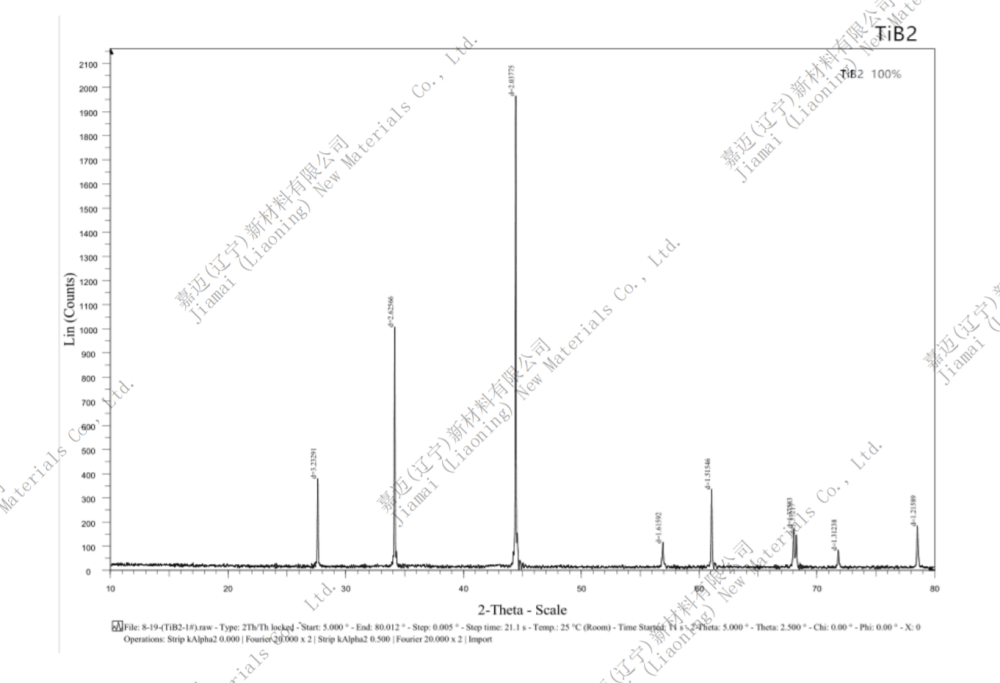

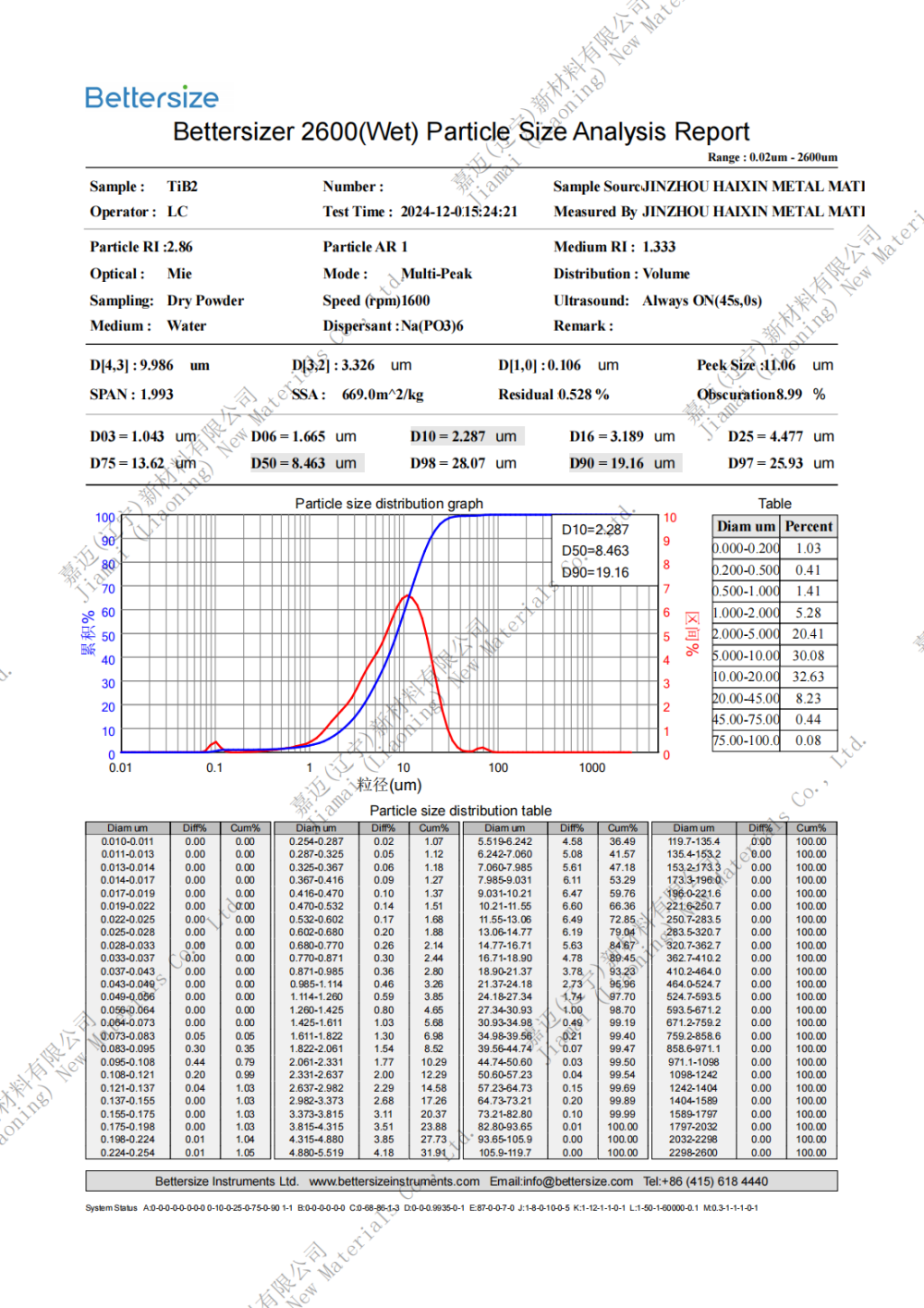
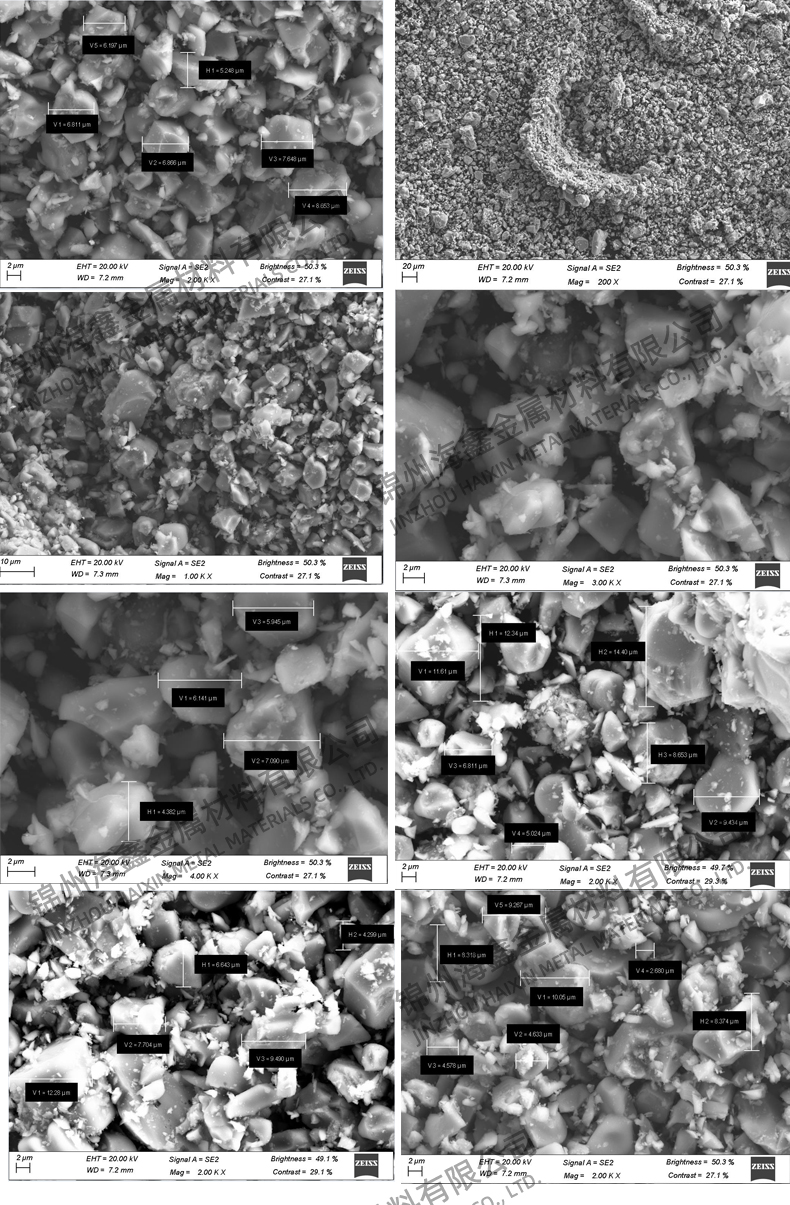

Titanium diboride (TiB2) is an inorganic compound with excellent physical and chemical properties, possessing a hexagonal crystal structure, good conductivity and metallic luster, as well as high hardness and brittleness. Its melting point is between 2900 ℃ and 3225 ℃, and its antioxidant temperature can reach 1100 ℃. It is stable in air, hydrochloric acid, and hydrofluoric acid, but reacts with alkali, nitric acid, and sulfuric acid.
Preparation method
Direct synthesis method: titanium powder and boron powder are directly combined at high temperature to form titanium diboride, but this method has high reaction temperature, high raw material price, and difficult process control.
Borothermic method: using titanium dioxide and boron carbide to react in a ball mill at a lower reaction temperature.
Melting electrolysis method: Titanium oxide reacts with alkali (or alkaline earth) metal borates and fluorites to form titanium diboride under melting electrolysis conditions.
Vapor deposition method: Using titanium tetrachloride and boron trichloride as raw materials, titanium diboride is deposited under the participation of hydrogen gas.
application area
Titanium diboride has been widely used in various fields due to its excellent physical and chemical properties
High temperature materials: used for making evaporation vessels, melting metal crucibles, aluminum electrolytic cell cathodes, etc.
Wear resistant materials: used for making wear-resistant parts, cutting tools, molds, etc. in high temperature and harsh environments.
Electronic materials: used for making electronic grade products, conductive ceramics, tool ceramics, etc.
Composite materials: used as reinforcing phases for high-performance applications such as bulletproof armor and electronic ceramic substrates.
New energy: Adding an appropriate amount of titanium diboride to the negative electrode material of lithium-ion batteries to improve the performance of the electrode material.









