English name: Magnesium diboride
Also known as magnesium boride
Chemical formula MgB2
Molecular weight 45.93
CAS login number 12007-25-9
Melting point 830 ℃
Density 2.57g/cm3

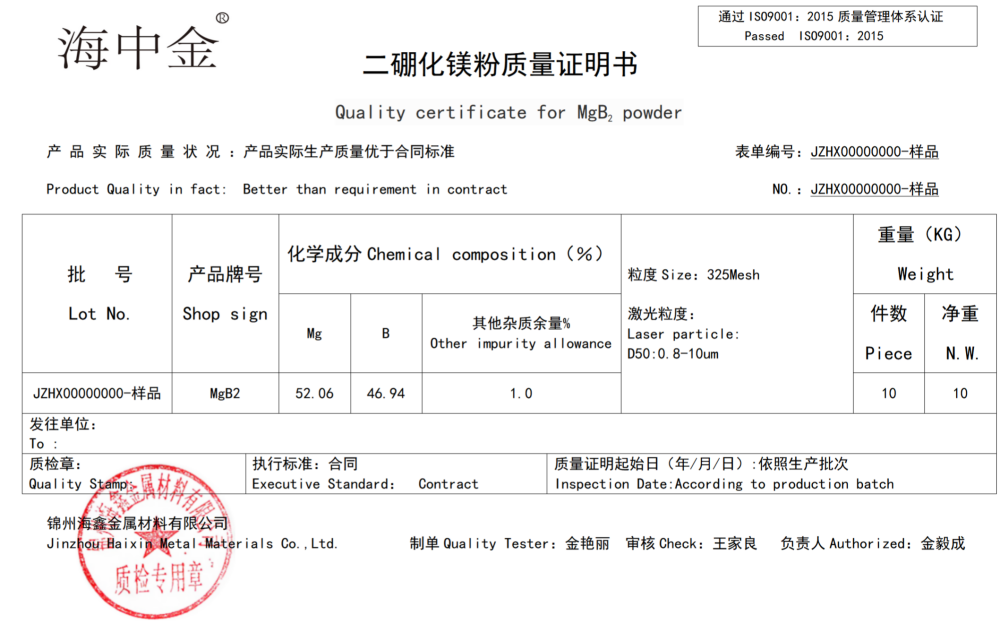

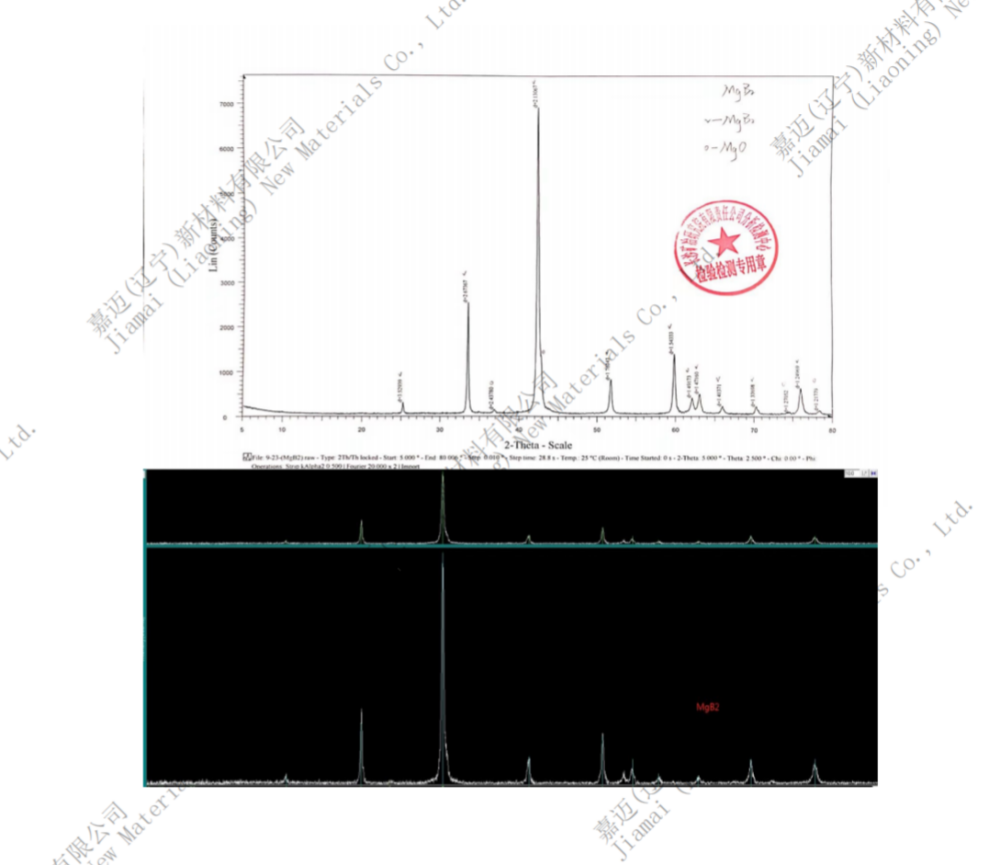



Chinese name: Magnesium diboride
English name: Magnesium diboride
chemical formula: MgB2
Molecular weight: forty-five point nine three
CAS : 12007-25-9
Melting point: 830℃
Density: 2.57g/cm3
nature:
1) The critical temperature refers to the critical temperature at which a material transitions from a non resistive state to a resistive state. Magnesium diboride has a high critical temperature of about 39K, which allows it to achieve superconductivity at liquid ammonia temperature. This relatively high critical temperature makes magnesium diboride a superconducting material with a wide range of applications. 2) The crystal structure of magnesium boride is a layered structure composed of alternating layers of magnesium and boron atoms. This structure gives magnesium diboride a unique electronic structure, including the bandgap (energy gap between energy bands) and the morphology of the Fermi surface. These characteristics have a significant impact on its superconducting properties. 3) In superconducting materials, mechanical stress often damages the superconducting properties. However, magnesium diboride has high compressibility and can resist a certain degree of external stress. This characteristic makes magnesium diboride more flexible and reliable in practical applications.
Purpose:
1) In the field of superconducting materials, it is used to prepare superconducting cables, superconducting magnets, and superconducting electronic devices;
2) As a combustion agent in solid fuel field as a propellant; It can also be used to prepare ceramic materials, catalysts, and metal boride coatings;
3) Excellent performance in optics, electronics, and magnetism, such as high optical transmittance and refractive index, can be used to prepare optical devices and window materials.