In recent years, advanced ceramics have shone brightly on the military stage. Due to its high specific stiffness, high specific strength, and chemical inertness in many environments, advanced ceramic made protective armor has strong resistance to intrusion, high portability, and comfort, making it an essential part of armor systems.

At present, bulletproof ceramic materials mainly include boron carbide (B4C), silicon carbide (SiC), and aluminum oxide (Al2O3). Among them, boron carbide is an important superhard material with hardness second only to diamond and cubic boron nitride in nature. It has the characteristics of high melting point, high modulus, low specific gravity, good self-lubricating properties, wear resistance, acid and alkali corrosion resistance, radiation resistance, neutron absorption, etc. It is a new type of high-performance engineering ceramic material with outstanding comprehensive performance. It has important applications in high-end bulletproof armor materials, high-end liquid and gas sealing materials, aerospace engine nozzles, high-end ceramic bearings, grinding media, polishing and precision grinding of hard materials, and other fields. In addition, boron carbide ceramics play an irreplaceable role in neutron absorption and shielding components of nuclear power reactors, and are an important national strategic material.
Due to its lightweight, high specific modulus, and good ballistic performance, boron carbide is considered an excellent bulletproof ceramic material with comprehensive performance. But its preparation is not easy because the boron carbide structure is an extremely difficult to sinter ceramic material, with covalent bonds reaching 93.94%, much higher than those of materials such as silicon carbide (88%) and silicon nitride (70%), which require the elimination of pores, grain boundaries, and volume diffusion in boron carbide to fully occur above 2200 ℃.
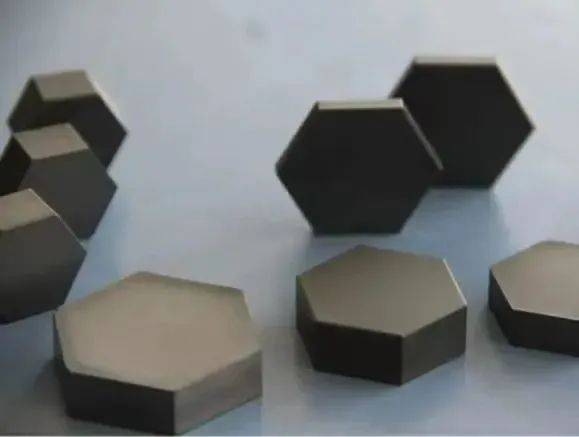

In general, ordinary boron carbide powder can only achieve a relative density of 80% -87% when sintered at 2250-2300 ℃ without pressure. Because sintering under such high temperature conditions results in rapid coarsening and growth of grains, which is not conducive to the elimination of pores and will generate a large number of residual pores, affecting the density of the material. At present, in order to improve the sintering density and performance of boron carbide ceramics, hot pressing sintering method is more commonly used. However, the cost and price of this process are very expensive, which limits the application of hot pressing boron carbide. It is mostly concentrated in the high-end protection market, such as the protection systems of helicopters, submarines, assault boats, and fighter jets. In the future, with the continuous progress and innovation of technology, it is believed that the performance and application fields of boron carbide materials will also be further expanded and improved.









